NETWORK
In information technology, a network are a series of points or nodes interconnected by communication paths. Networks can interconnect with other networks and contain subnetworks. The most common topology or general configurations of networks include the Bus Network, Star Network, Token Ring Network, and Mesh topologies Network. Networks can also be characterized in terms of spatial distance as Local Area networks (LANs), Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs), and Wide Area Networks (WANs). A given network can also be characterized by the type of data transmission technology in use on it . For example, a TCP/IP or Systems Network Architecture network; by whether it carries voice, data, or both kindes of signals; by who can use the network (public or private); by the usual nature of its connections (dial-up ore switched, dedicated or nonswitched, or virtual connections); and by the types of physical links (for example, Fiber Optical Cable, Coaxial Cable, and Twisted Pair Cable). Large telephone networks and networks using their infrastructure, such as the Internet have sharing and exchange arrangements with other companies so that larger networks are created.
TELECOMMUNICATION
Telecommunication are the transmission of signals over a distance for the purpose of communication. In earlier times, this may have involved the use of Smoke Signals, Drums, Semaphore, Flags or Heliograph. In modern times, telecommunication typically involves the use of electronic devices such as Telephones, Television, Radio or Computers.
The evolution in telecommunication: from wire to wireless
WIRED TECHNOLOGIES
(i.) Twisted Pair Wire
*Twisted pair wire is the most widely used medium for telecommunication. Twisted-pair wires are ordinary telephone wires which consist of two insulated copper wires twisted into pairs and are used for both voice and data transmission. The use of two wires twisted together helps to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic induction. The transmission speed ranges from 2 million bits per second to 100 million bits per second.
(ii.) Coaxial Cable
*Coaxial cable is widely used for cable television systems, office buildings, and other worksites for local area networks. The cables consist of copper or aluminum wire wrapped with insulating layer typically of a flexible material with a high dielectric constant, all of which are surrounded by a conductive layer. The layers of insulation help minimize interference and distortion. Transmission speed range from 200 million to more than 500 million bits per second.
(iii.) Fiber-Optical Cable
*Optical fiber cable consists of one or more filaments of glass fiber wrapped in protective layers. It transmits light which can travel over extended distances without signal loss. Fiber-optic cables are not affected by electromagnetic radiation. Transmission speed may reach trillions of bits per second. The transmission speed of fiber optics is hundreds of times faster than for coaxial cables and thousands of times faster than for twisted-pair wire.
WIRELESS TECHNOLOGIES
(i.) Terrestrial Microwave
*Terrestrial microwaves use Earth-based transmitter and receiver. The equipment look similar to satellite dishes. Terrestrial microwaves use low-gigahertz range, which limits all communications to line-of-sight. Path between relay stations spaced approx. 30 miles apart. Microwave antennas are usually placed on top of buildings, towers, hills, and mountain peaks.
(ii.) Communications Satellites
*The satellites use microwave radio as their telecommunications medium which are not deflected by the Earth's atmosphere. The satellites are stationed in space, typically 22,000 miles above the equator. These Earth-orbiting systems are capable of receiving and relaying voice, data, and TV signals.
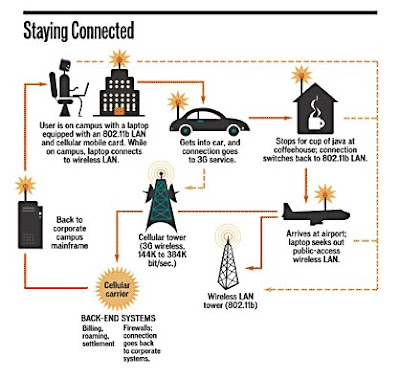
(iii.)Wireless LANs
*Wireless local area network use a high-frequency radio technology similar to digital cellular and a low-frequency radio technology. Wireless LANs use spread spectrum technology to enable communication between multiple devices in a limited area. An example of open-standards wireless radio-wave technology is IEEE 802.11b.
(iv.)Bluetooth
*A short range wireless technology. Operate at approx. 1Mbps with range from 10 to 100 meters. Bluetooth is an open wireless protocol for data exchange over short distances.
(v.)The Wireless Web
*The wireless web refers to the use of the World Wide Web through equipments like cellular phones, pagers,PDAs, and other portable communications devices. The wireless web service offers anytime/anywhere connection.